Current Research
Ryanodine receptor structure and function, molecular mechanisms of cardiac and skeletal muscle function, heart failure, arrhythmias, muscular dystrophy, and sarcopenia
A major focus of the laboratory is the study of mechanisms that regulate muscle contraction. In particular we use a variety of techniques including molecular biology, biophysics, cell biology, imaging (Live5 Zeiss Confocal), and structural biology to gain better understandings of the regulation of calcium release channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum that control excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in cardiac and skeletal muscle. There are opportunities for graduate students and postdoctoral fellows to head their own projects using any of the various techniques that we employ to examine the regulation of calcium signaling and muscle function in normal and diseased states. In addition the laboratory has developed numerous genetic mouse models (primarily knock-ins and knock-outs) that are available to address specific questions concerning the regulation of key signaling pathways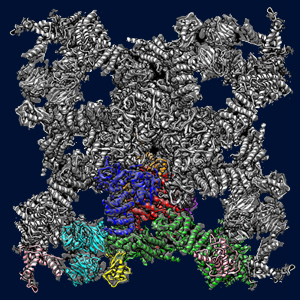 that control muscle contraction - in both cardiac and skeletal systems.
that control muscle contraction - in both cardiac and skeletal systems.
Much of thework in the laboratory is "translational" in
that it leads directly to understanding the molecular basis of human diseases including heart failure and sudden cardiacdeath. In addition, novel therapeutic approaches are being tested including those that fix the "leak" in the RyR2 calcium release channel that causes heartfailure and sudden cardiac death.
 read more
read more
In addition, there are projects focusing on gaining better understandings of cardiac muscle growth and excitability, T cell and B cell activation, as well as vascular smooth muscle proliferation. The latter project has lead directly to the development of the drug eluting stents that are
currently used for patients with coronaryartery disease. His approach is responsible for the first drug eluting stent used to prevent coronary artery stent restenosis.
 read more
read more
Selected Publications
Brillantes AB, Ondrias K, Scott A, Kobrinsky E, Ondriasova E, Moschella MC, Jayaraman T, Landers M, Ehrlich BE, Marks AR.
Stabilization of calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function by FK506-binding protein. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):513-23.
Jayaraman T, Ondrias K, Ondriasova E, Marks AR.
Regulation of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1996 Jun 7;272(5267):1492-4.
Marx SO, Ondrias K, Marks AR.
Coupled gating between individual skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channels (ryanodine receptors) Science. 1998 Aug 7;281(5378):818-21.
Marx SO, Reiken S, Hisamatsu Y, Jayaraman T, Burkhoff D, Rosemblit N, Marks AR.
PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell. 2000 May 12;101(4):365-76.
Marx SO, Kurokawa J, Reiken S, Motoike H, D'Armiento J, Marks AR, Kass RS.
Requirement of a macromolecular signaling complex for beta adrenergic receptor modulation of the KCNQ1-KCNE1 potassium channel. Science. 2002 Jan 18;295(5554):496-9.
Wehrens XH, Lehnart SE, Huang F, Vest JA, Reiken SR, Mohler PJ, Sun J, Guatimosim S, Song LS, Rosemblit N, D'Armiento JM, Napolitano C, Memmi M, Priori SG, Lederer WJ, Marks AR.
FKBP12.6 deficiency and defective calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function linked to exercise-induced sudden cardiac death. Cell. 2003 Jun 27;113(7):829-40.
Wehrens XH, Lehnart SE, Reiken SR, Deng SX, Vest JA, Cervantes D, Coromilas J, Landry DW, Marks AR.
Protection from cardiac arrhythmia through ryanodine receptor-stabilizing protein calstabin2. Science. 2004 Apr 9;304(5668):292-6.
Lehnart, S. , Wehrens, X., Reiken, S., Warrier, S., Belevych, AE, Harvey, RD, Richter, W., Jin, S.- L. C., Conti, M., and Marks, AR.
Phosphodiesterase 4D deficiency in the ryanodine receptor complex promotes heart failure and arrhythmias. Cell. 2005 Oct. 7; 123:25-35
Bellinger, AM, Reiken, SR, Dura, M, Murphy, P, Deng, S-X, Neiman, D, Lehnart, S, Samaru, M, Lacampagne, A, and Marks, AR (2008)
Remodeling of ryanodine receptor complex causes "leaky" channels: a molecular mechanism for decreased exercise capacity PNAS 105: 2198-2202
Bellinger, AM, Reiken, S, Carlson, C, Mongillo, M, Liu, X, Rothman, L, Matecki, S, LaCampagne, A, and Marks, AR (2009)
Hypernitrosylated ryanodine receptor/calcium release channels are leaky in dystrophic muscle. Nature Medicine 15:325-330
Shan, J., Kushnir, A., Betzenhauser, M., Reiken, S., Li, J., Lehnart, S.E., Lindegger, N., Mongillo, M., Mohler, P.J., Marks, A.R. (2010) Phosphorylation of the Ryanodine Receptor Mediates the Cardiac Fight or Flight Response in Mice J. Clin. Invest. 120: 4375-87.
Shan, J., Betzenhauser, M., Kushnir, A., Reiken, S., Meli, A., Wronska, A., Dura, M., Chen, B.-X., Marks, A.R. (2010) Role of Chronic Ryanodine Receptor Phosphorylation in Heart Failure and Beta-adrenergic Receptor Blockade in Mice J. Clin. Invest. 120: 4388-98.
Andersson DC, Betzenhauser MJ, Reiken S,
Meli AC, Umanskaya A, Xie W, Shiomi T, Zalk R, Lacampagne A, Marks AR. Ryanodine receptor oxidation causes intracellular calcium leak and
muscle weakness in aging. Cell Metab. 2011 Aug 3;14(2):196-207. PMID: 21803290
Liu, X., Betzenhauser, M.J., Reiken, S., Meli, A.C., Arancio, O., Chen B.-X., Marks AR (2012) Role of Leaky Neuronal Ryanodine Receptors in Stress-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction Cell 150, 1055–1067.
Ran Zalk, Oliver B. Clarke, Amédée des Georges, Robert A. Grassucci, Steven Reiken, Filippo Mancia, Wayne A. Hendrickson, Joachim Frank, Marks, A.R. (2014) Structure of a mammalian ryanodine receptor Nature 2014 Dec 1. doi: 10.1038/nature13950. [Epub ahead of print]
Waning DL, Mohammad KS, Reiken S, Xie W, Andersson DC, John S, Chiechi A, Wright LE, Umanskaya A, Niewolna M, Trivedi T, Charkhzarrin S, Khatiwada P, Wronska A, Haynes A, Benassi MS, Witzmann FA, Zhen G, Wang X, Cao X, Roodman GD, Marks AR, Guise TA
Excess TGF-Beta mediates muscle weakness associated with bone metastases in mice.
Nature Medicine, 2015 Oct 12 [Epub ahead of print] PMID:26457758
des Georges A, Clarke OB, Zalk R, Yuan Q, Condon KJ, Grassucci RA, Hendrickson WA, Marks AR,
Frank, J Structural Basis for Gating and Activation of RyR1.
Cell 2016 Sep 22;167(1):145-157.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.075. PMID:27662087
Honors
| 1995 |
American Society of Clinical Investigation (ASCI) |
| 1999 |
Association of American Physicians (AAP)
|
| 2002-2007 |
Editor-in-Chief - The Journal of Clinical Investigation |
| 2004 |
Member, Institute of Medicine, National Academy of Sciences
|
| 2005 |
Fellow, American Academy of Arts and Sciences |
| 2005 |
Member, National Academy of Sciences, USA |
| 2005 |
AHA,Basic Research Prize |
| 2009 |
Doctor of Science, Honoris causa, Amherst College |
| 2010 |
Stanley J. Korsmeyer Award, ASCI
|
| 2011 |
Robert J. and Claire Pasarow Award in Cardiovascular Disease Research |
| 2011 |
Ellison Medical Foundation Senior Scholar in Aging |
| 2015 |
Ulf von Euler lecturer Karolinska Institute |
| 2016 |
Glorney-Raisbeck Award, NY Academy of Medicine |
| 2016 |
Docteur Honoris causa, de l’Université de Montpellier |